Ind As 34
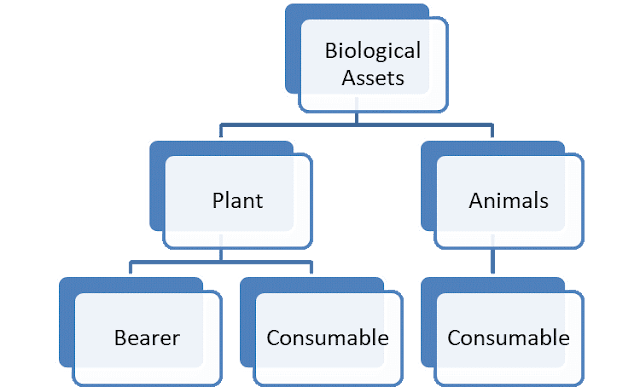
Ind As 34- Interim Financial Statement Presentation of item in financial statement is described in three different Ind AS standards, Known as: Ind As 1 (As-1): Presentation of general purpose Financial statement Ind As 34 (AS 25): Interim Financial statement Ind As 7 (AS 3): Cash Flow statement Here we will discuss about the Ind As 34 which is mostly similar to AS 25 which describes about Interim Financial Statement. Meaning of Interim Report: Interim report is the reporting of the financial Information for less than 12 months. Important Note: First account may be of less than 12 months but can’t be classified as interim report. According to Ind As- 34 Interim Financial statements includes: 1. Balance sheet 2. Profit and loss account . Comprehensive Income .Other comprehensive Income 3. Cash flow statement 4. Statement of ...